Support your cells with omega fatty acids.
Good fats and oils are vital for our body. They perform key tasks for our immune and nervous systems, metabolism, hormone balance and a strong heart. Our body cannot produce omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids itself. We must obtain them daily from our diet.
Three different forms of omega-3 fatty acid are found in food:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid),
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid) and
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid).
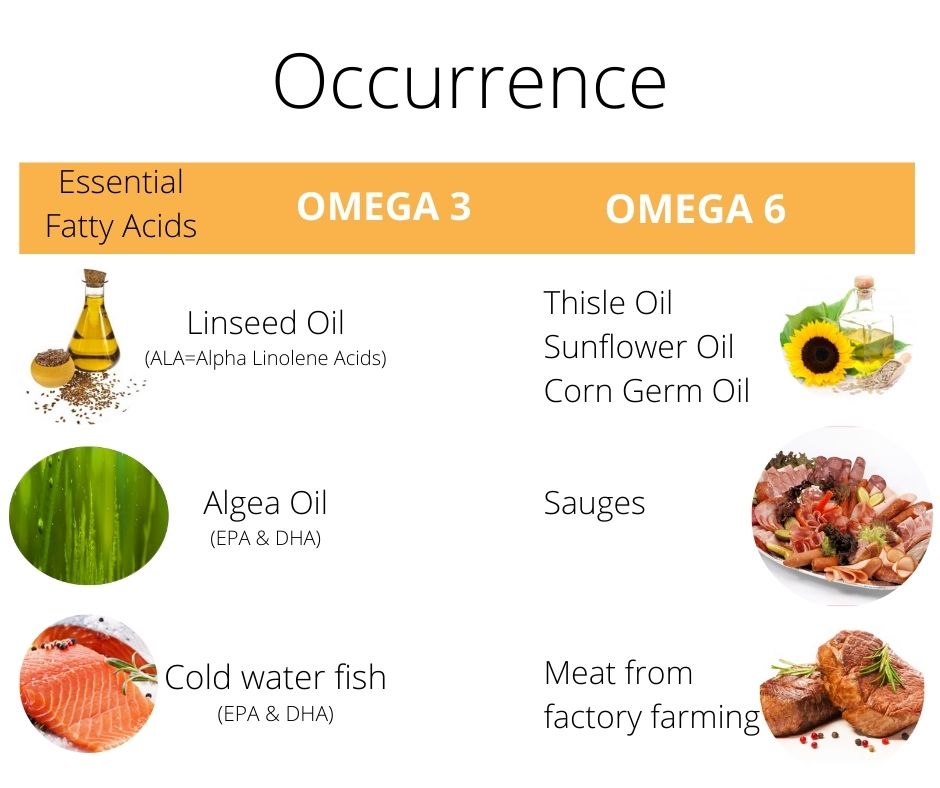
We absorb alpha-linolenic acid mainly through vegetable oils. Especially oils from flaxseed, rapeseed, walnuts and soy provide larger amounts.
* DHA = Docosahexaenoic acid
The omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA are predominantly found in fatty marine fish, e.g. herring, salmon, tuna, sardine and mackerel.
They are found only in small amounts in freshwater fish such as trout or carp and in land animals. Depending on the fishing area and season, the amount of omega-3 fatty acids in fish can vary considerably.
Fatty acids and inflammation
The fact that today’s diet is rich in omega-6 and at the same time poor in omega-3 fatty acids plays an important role in the topic of inflammation. This is because inflammation is triggered, among other things, by the formation of inflammatory factors, formed from the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid (AA).
In contrast, anti-inflammatory messengers are formed by the body from the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
For the conversion of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids into the pro- and anti-inflammatory messengers, respectively, the body needs the same enzyme system – in which the two types of fatty acids consequently behave like counterparts. And because omega-6 intake is so high these days, the formation of anti-inflammatory messengers from omega-3 fatty acids is blocked. With corresponding negative consequences for health.
Professional societies recommend an intake of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in a maximum ratio of 5:1, but the actual ratio is about 25:1.
The consequence of this imbalance: inflammations are not stopped sufficiently. This can lead to chronic inflammatory diseases.
What are the OMEGA 3 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 9 fatty acids derived from?
If you do not like fatty, freshly caught cold water fish, you can supply omega-3 fatty acids via algae oils. The fatty cold water fish eats this algae and deposits it in the fatty tissue. Not entirely unproblematic, in addition to overfishing, are the environmental pollutants, such as microplastics, heavy metals, pesticides, antibiotics, …etc., which are also deposited in the fat

To protect the fatty acids from oxygen (oxidative stress), the encapsulated form, is the best solution.
What are the effects of Omega 3 fatty acids, DHA & EPA?
The OMEGA-3 fatty acids DHA + EPA contribute to the normal functioning of the heart. DHA supports the maintenance of normal brain activity and visual function.
